"Hao" Product – Geomembrane for Oxidation Ponds
Common Challenges of Conventional Geomembranes
1. Environmental Stress Cracking (ESC)
HDPE geomembranes: Resin density range 0.935–0.940 g/cm³, high crystallinity.
LLDPE geomembranes: Resin density 0.919–0.925 g/cm³, low crystallinity.
For landfill capping, ESC resistance is a critical performance requirement.
2. Differential Settlement
Post-closure, uneven waste settlement creates localized depressions.
Capping materials undergo large deformations as terrain shifts.
Low deformability leads to stress buildup, causing cracks.
3. Membrane Bulging & Stress Concentration
Gas accumulation beneath the membrane forms localized bulges, leading to tensile deformation or rupture.
4. Biogas Pressure Fluctuations & Fatigue Failure
Biogas pressure variations (typically 5–10 kPa) cause repeated expansion/contraction.
Welded seams are prone to fatigue cracking.
Features of Oxidation Pond-Specific Geomembrane
1. Superior Performance
In landfill capping, LLDPE geomembranes match HDPE in:
High tensile strength
Excellent water vapor barrier
Superior methane gas resistance
Fully complies with landfill capping technical standards.
2. High Multiaxial Elongation
LLDPE outperforms HDPE in landfill applications due to:
Differential settlement
Methane gas generation during waste decomposition.
Key elongation comparison:
HDPE: ~15%
LLDPE: ≥30%
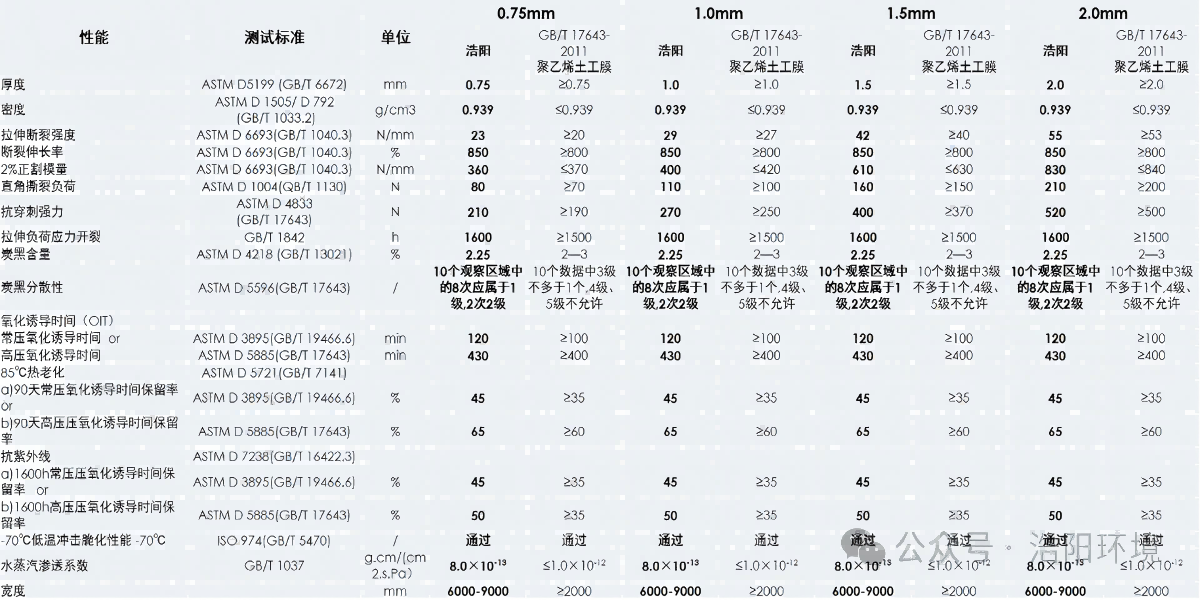
Technical Specifications