Geomembrane Functional Properties and Engineering Applications
Ⅰ. Basic definition and characteristic
Geotextile is a permeable textile made of synthetic fibers such as polypropylene (PP), polyester or polyethylene (PE), which is formed into a stable structure through woven or non-woven processes. Its core characteristics include controlled porosity (allowing water to pass but blocking soil particles), biodegradability and chemical resistance (adapting to pH 3-11 environment). It mainly plays the role of functions of separating soil layers, strengthening foundations, guiding drainage and controlling erosion.
Ⅱ. Engineering functions and application system
Structural stability function
Separation function: laid between road subgrades or railway ballast layers to prevent fine-grained soil from invading coarse aggregate and avoid settlement and deformation (especially suitable for low-standard roads such as logging roads).
Reinforcement function: high-strength woven fabrics disperse load stress, improve the bearing capacity of soft soil foundations, and are used for retaining walls and slope reinforcement.
Hydrological management function
Filtration control: non-woven fabrics act as dynamic filters in the seepage area of dams, allowing water to pass but intercepting soil particles to prevent pipe burst damage.
Drainage and diversion: needle-punched felt structures quickly drain groundwater and are used in tunnel linings and retaining wall back drainage systems.
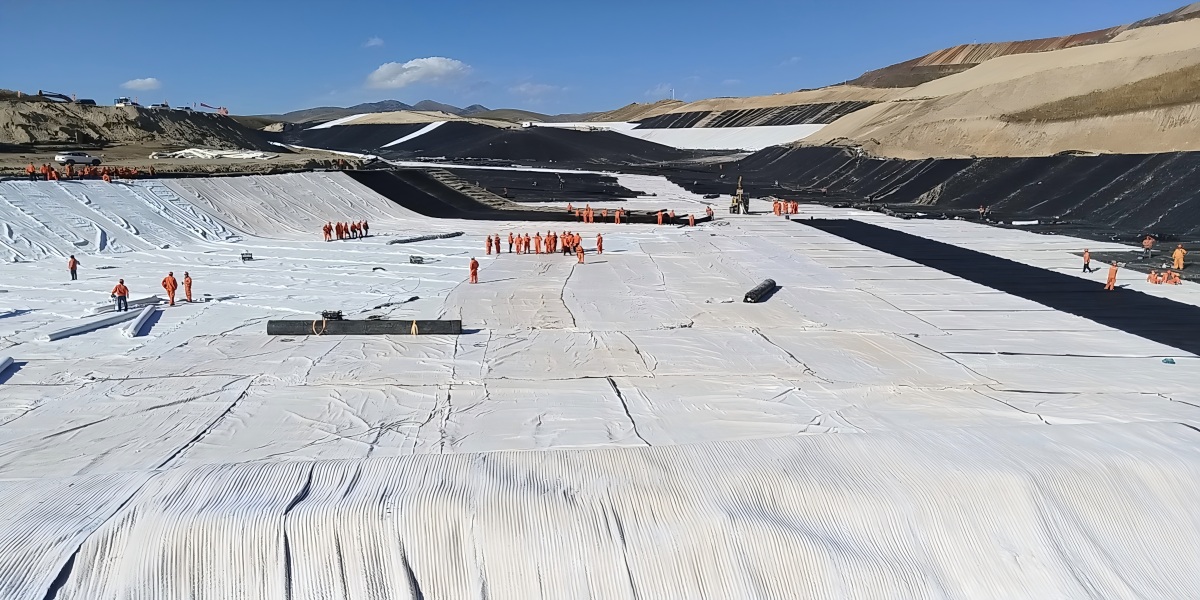
Impermeable sealing: geomembranes are used as landfill liners or reservoir impermeable layers to block the migration of harmful leachate.
Environmental protection function
Erosion protection: composite geotextiles resist wave scouring and are used in coastal projects such as gabion slope protection, requiring both high strength and permeability.
Vegetation management: Lightweight nonwovens inhibit weed growth (permeable and breathable but light-blocking) and promote nutrient absorption of target crops.
Ⅲ. Special technologies for dam construction
Geosynthetics play a triple role in water conservancy projects:
Anti-filter layer construction: Nonwovens control core wall seepage and balance water permeability and soil retention.
Isolation: Prevent fill materials from piercing the impermeable .
Construction period protection: Degradable natural fiber cloth temporarily covers the slope to reduce rainwater erosion until vegetation recovers.
Damage during installation and long-term blockage risks need to be avoided through professional design.
Ⅳ. Material evolution and performance specifications
Historical development: In the 1950s, RJ Barrett developed monofilament woven filter cloth for seawall projects, and in the 21st century, synthetic polymers (polypropylene/polyester) completely replaced natural fibers (straw mats/flax).
Durability benchmark:
Lifespan>20 years (UV stabilizer enhanced material + standard welding)
Damage repair uses hot melt patch or chemical bonding, and negative pressure testing is required after repair
Chemical resistance:
Standard HDPE is acid and alkali resistant (pH 3-11), XR-5 formula is resistant to hydrocarbon solvents
Verification is based on ASTM D5322 accelerated aging test
Ⅴ. Industry practice reference
India Ocean Global provides a full range of geotextile/membrane solutions, with 21 years of technical accumulation covering roads, water conservancy and environmental protection projects, and has passed the ISO quality certification system.
Ⅵ. Frequently asked questions
Q1: How to ensure the life of the anti-seepage system?
High-quality HDPE membrane can reach 30 years under standard construction, key control points: ① UV protection layer above 2mm ② Anchor trench depth>0.8m
Q2: How to remedy construction damage?
Extrusion welding is used for repair of pore size ≤6mm, and hot melt lap joints are required after cutting off the damaged part>6mm
Q3: How to evaluate the risk of chemical corrosion?
Select materials based on the media type: Polypropylene is better at acid resistance than polyester, and HDPE’s stress cracking resistance is the key indicator