Application of Geomembranes in Modern Engineering Fields
In modern engineering fields such as water conservancy, environmental protection, and transportation, a seemingly inconspicuous but crucial material silently guards engineering safety and the environment - it is geomembrane, a flexible anti-seepage isolation barrier based on high molecular polymers. According to the national standard "GB/T 17643-2011 Geosynthetics Polyethylene Geomembrane", geomembranes are clearly defined as "membrane-like geosynthetics made of polymers and basically impermeable", and their core function is to effectively block the migration of liquids (water, chemical solutions) and gases.
1. Classification by Material and Structure
- By main material:
PE (polyethylene) membrane: the most widely used, including:
HDPE (high-density polyethylene) membrane: high strength, strong chemical corrosion resistance, excellent anti-ultraviolet aging performance, suitable for harsh environments such as landfills, hazardous waste disposal sites, and large reservoirs.
LDPE (Low-density polyethylene) and LLDPE (Linear low-density polyethylene) films: Softer, high elongation, strong adaptability to deformation, often used in aquaculture, artificial lakes, channels and other projects with high requirements for anti-seepage but relatively mild environment.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) film: Good flexibility, can be made into wider products, easy to weld, more applications in the early days, but low temperature resistance and long-term anti-aging are usually weaker than HDPE.
EVA film: Excellent elasticity and low temperature resistance, especially suitable for cold areas or occasions with high flexibility requirements.
- According to the structural form:
Smooth geomembrane: Smooth surface and relatively low friction coefficient.
Rough geomembrane (single rough/double rough): The surface is made rough by special process, which significantly increases the friction coefficient with soil or geotextile and improves the stability of slope.
Composite geomembrane: The geomembrane and geotextile are combined by thermal compounding or gluing (such as two cloths and one membrane, one cloth and one membrane). Geotextiles provide protection, drainage and reinforcement, with better comprehensive performance and wide application.
2. The Main Advantages of Geomembranes
- Excellent anti-seepage performance: The permeability coefficient is extremely low (usually <10^-13 cm/s), which is hundreds of times or even higher than that of natural anti-seepage materials such as clay, and can be called "watertight".
- High strength and durability: HDPE membranes in particular have excellent tensile, tear and puncture resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, UV aging resistance, and a service life of more than 50 years.
- Lightweight and economical: Light weight, convenient transportation and laying; the unit area cost is often lower than the traditional clay anti-seepage solution, saving project investment.
- Efficient construction: Standardized factory production, large width, mature on-site welding technology, and fast construction speed.
- Strong adaptability: Good flexibility enables it to adapt to uneven settlement and certain deformation of the foundation; the rough surface design meets the stability requirements of steep slopes.
- Environmentally friendly: Effectively prevent pollutant leakage, protect groundwater and soil; the material itself is non-toxic and harmless.
3. Six Application Scenarios of Geomembranes
- Environmental protection projects: base and cover anti-seepage layers of domestic waste landfills, industrial solid waste/hazardous waste disposal sites, and sewage regulating pools/treatment pools (core applications).
- Water conservancy projects: anti-seepage linings of reservoirs, channels, and dams; anti-seepage of artificial lakes and landscape water bodies; anti-seepage of sluice gates and cofferdams.
- Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery: anti-seepage of aquaculture ponds (shrimp ponds, fish ponds); anti-seepage of irrigation channels; linings of reservoirs and biogas pools.
- Mining projects: anti-seepage of bases of heap leaching pools and tailings ponds; linings of dissolution pools and evaporation pools.
- Construction projects: moisture and anti-seepage of underground structures (basements, tunnels); waterproof layers of roof gardens; anti-seepage of roadbed isolation.
- Transportation projects: isolation and drainage of roadbeds of highways and railways; anti-seepage of tunnels.
4. Key Steps for Construction and Laying
- Preliminary preparation:
Foundation treatment: Level and compact the site, remove sharp stones, tree roots and other debris, ensure that the foundation is solid and the slope is smooth in accordance with the design requirements. Special geology (such as collapsible loess) requires special treatment.
Material acceptance and storage: Accept geomembrane and auxiliary materials (such as welding rods) according to design requirements, with complete certificates and test reports. Store in a flat site, avoid sun and rain, and stay away from fire.
- Laying:
Cutting planning: Plan the laying plan according to the site size and design drawings, and minimize on-site welds. Reserve the expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes and stress.
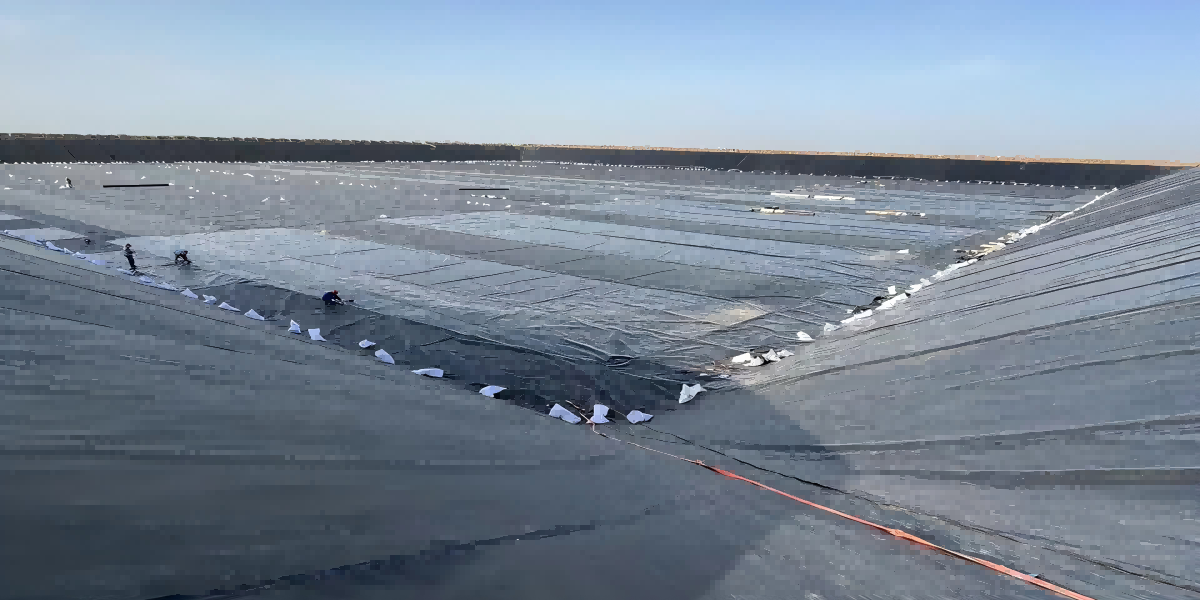
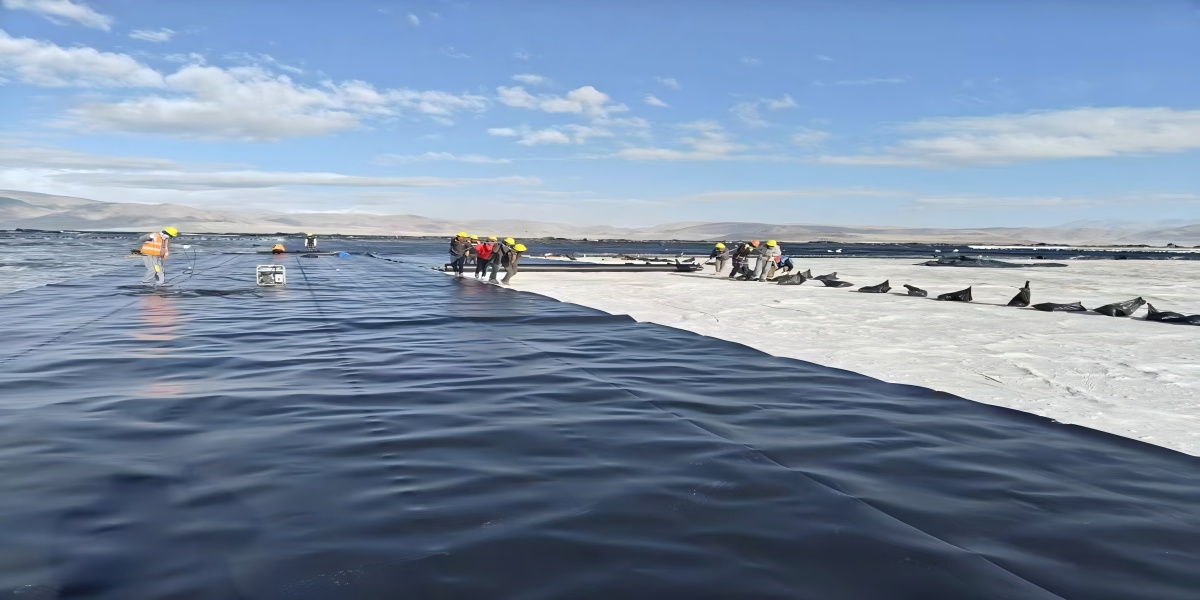
Laying operation: Usually laid from the lowest point to the highest point. The membrane should be naturally relaxed and smoothly spread to avoid artificial wrinkles and stress concentration. When laying on the slope, it is advisable to proceed from top to bottom, and take measures (such as sandbags) for temporary anchoring. The overlap width of the membrane meets the requirements (generally 10-15cm for smooth surface, and larger for rough surface).
Protective layer: During the laying process, the protective layer (such as geotextile or sand layer required by the design) should be covered in time to prevent the membrane from being blown, punctured or aged by exposure to the sun.
- Welding (core process):
Method selection: Hot wedge welding (double-track fusion welding) and extrusion welding gun welding (single-track welding, used for T-type, repair, and complex parts) are mainly used.
Parameter control: The temperature, speed and pressure of the welding machine are strictly set according to the type, thickness, ambient temperature and humidity of the membrane material. Before formal welding, a trial welding must be carried out, and the trial welding samples must be subjected to destructive testing (such as shear and peeling tests) before formal welding can be carried out.
Weld seam detection: Use air pressure detection (enclosed cavity formed by double-track welding) or electric spark detection (for extrusion welds) to detect the tightness of the weld seams. Unqualified welds must be repaired and re-inspected in time.
- Anchoring
Backfill and cover: After acceptance, the protective layer and upper filler are backfilled in layers according to the design requirements to avoid heavy machinery working directly on the membrane to prevent damage.
Quality inspection and acceptance: The whole process (materials, foundation, welding, anchoring, covering) is strictly controlled and recorded, and the final acceptance is carried out according to the specification requirements.
5. Why Choose Haoyang Enivronmental?
- Advanced Material Science: Choose Haoyang for engineered geomembranes with molecularly stabilized formulations achieving 0 05 perm vapor barrier rates and 98 UV resistance surpassing GRI GM13 standards ensuring decades of reliable containment
- Certified Quality Assurance: Our ISO 9001 certified manufacturing utilizes 100 virgin resins with batch traceability and third party lab validation guaranteeing consistent thickness tolerance within 3 across all 1 5mm HDPE liners
- Engineering Precision: Proven installation expertise through patented 10 meter wide seamless welding technology reduces field joints by 70 lowering leakage risks while accommodating 380 elongation for subgrade settlement.
- Global Performance Validation: Products field tested in extreme environments from Chilean mining tailings ponds to Thai monsoon canals with zero reported failures across 300 projects since 2008.
- Cost Efficiency: Wide roll formats and robotic welding cut installation time 50 delivery 30 lifecycle savings versus conventional methods confirmed by Indonesia dam project case studies.
- Sustainable Partnership: Dedicated R&D team provides site specific solutions including seismic zone reinforcement designs and NSF 61 certified potable water linings supporting your ESG goals with low carbon footprint geosynthetics.
Geomembrane has become an indispensable "anti-seepage guard" in modern engineering with its excellent anti-seepage performance, excellent physical and chemical stability and convenient construction. From the environmental protection barrier to protect the green waters and green mountains, to the water lifeline to ensure agricultural irrigation, to the isolation foundation to support transportation infrastructure, the application of geomembranes is constantly expanding. With the advancement of material technology and the improvement of construction technology, geomembranes will play a more critical role in building a safe, green and sustainable engineering system, and provide a solid guarantee for the harmonious coexistence of human engineering and the natural environment.